Prostate Cancer: A Brief Overview
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, affecting the prostate gland—a walnut-shaped organ that plays a vital role in male reproductive health. As a medical oncologist specializing in cancer care, I aim to provide a clear understanding of prostate cancer and its treatment options, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and emerging molecular agents.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer typically grows slowly and may remain confined to the prostate gland for years without causing symptoms. However, aggressive types can spread quickly, requiring prompt treatment. Risk factors include age, family history, and genetic predispositions such as BRCA mutations.
Common Symptoms of Prostate Cancer:
- Difficulty urinating or weak urine flow
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pelvic discomfort
- Bone pain (in advanced stages)
- Erectile dysfunction
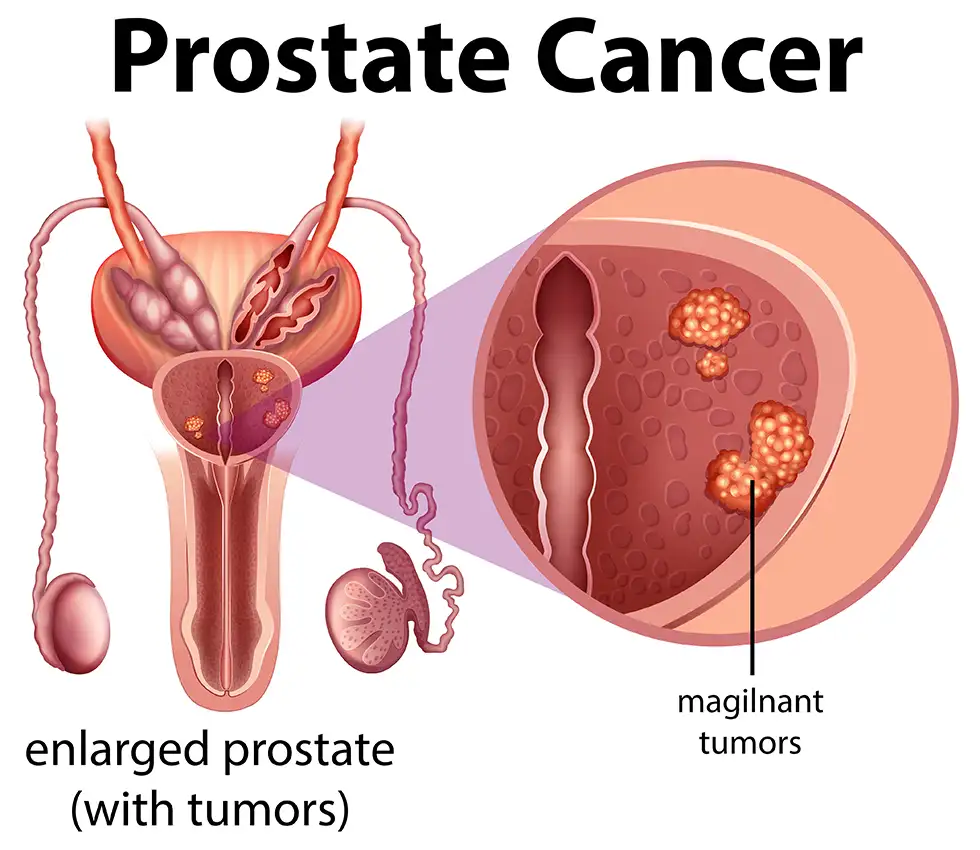
Stages of Prostate Cancer
Treatment strategies for prostate cancer depend on the stage of the disease:
- Localized (Stages I-II): Cancer is confined to the prostate gland.
- Locally Advanced (Stage III): Cancer has spread to nearby tissues.
- Advanced or Metastatic (Stage IV): Cancer has spread to lymph nodes, bones, or other organs.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
A multidisciplinary approach involving urologists, radiation oncologists, and medical oncologists ensures the best outcomes. Let’s explore the available treatments:
Active Surveillance and Watchful Waiting
For men with low-risk or early-stage prostate cancer, active surveillance may be recommended. This approach involves regular monitoring through PSA tests, digital rectal exams (DRE), and biopsies to track cancer progression without immediate treatment.
Surgery: Radical Prostatectomy
Surgical removal of the prostate gland and nearby lymph nodes is a curative option for localized prostate cancer. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery has made this procedure less invasive, reducing recovery time and complications.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It can be used alone for localized disease or in combination with hormone therapy for advanced cases.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Focused radiation is delivered from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: Radioactive seeds are implanted directly into the prostate gland.
Hormone Therapy (Androgen Deprivation Therapy)
Prostate cancer cells depend on androgens like testosterone to grow. Hormone therapy reduces androgen levels or blocks their effect on cancer cells.
- LHRH Agonists/Antagonists: Drugs like leuprolide suppress testosterone production.
- Anti-Androgens: Medications such as bicalutamide block the action of testosterone on cancer cells.
- Orchiectomy: Surgical removal of the testes to reduce androgen levels is an irreversible option.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is typically reserved for advanced or hormone-resistant prostate cancer. It involves systemic drugs that kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- Docetaxel and Cabazitaxel: These are the most commonly used chemotherapy agents for metastatic prostate cancer.
- Combination Therapy: Chemotherapy may be combined with hormone therapy to improve survival in men with metastatic disease.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific genetic mutations or proteins driving cancer growth.
- PARP Inhibitors: For men with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, drugs like olaparib and rucaparib have shown significant benefits.
- Radiopharmaceuticals: Radium-223 selectively targets cancer that has spread to bones, providing pain relief and prolonging survival.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
- Sipuleucel-T (Provenge): This FDA-approved cancer vaccine uses a patient’s immune cells to target prostate cancer. It is primarily used in metastatic cases.
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Although not widely used for prostate cancer, pembrolizumab has shown promise in certain genetic subgroups, such as those with MSI-H or dMMR tumors.
Emerging Molecular Agents
Advances in genomics and precision medicine have introduced new agents targeting prostate cancer at a molecular level.
- Androgen Receptor Signaling Inhibitors: Drugs like enzalutamide and apalutamide provide potent inhibition of androgen receptor pathways.
- PSMA-Targeted Therapies: Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted drugs like lutetium-177 PSMA are emerging as promising treatments for advanced prostate cancer.
- Combination Strategies: Ongoing clinical trials are exploring combinations of immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy for improved outcomes.
Comprehensive Care for Prostate Cancer
Treatment goes beyond addressing the disease. Managing the side effects of therapy and supporting the patient’s overall well-being is equally important.
- Bone Health: Advanced prostate cancer often spreads to bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Bisphosphonates or denosumab may be prescribed to strengthen bones.
- Quality of Life: Rehabilitation programs can help manage urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction after surgery or radiation therapy.
- Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and regular exercise play a vital role in recovery and overall health.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Thanks to advances in screening and treatment, the survival rates for prostate cancer have significantly improved. Early detection offers the best chance for a cure, while advanced treatments provide hope even for metastatic cases.
Why Choose Expert Care?
Prostate cancer treatment is not one-size-fits-all. It requires a personalized approach based on the patient’s stage, age, health status, and preferences. A team of experienced specialists ensures that each patient receives the most effective and compassionate care.
Final Thoughts
Prostate cancer treatment has evolved tremendously, with new therapies offering hope to patients at every stage of the disease. Whether through surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or cutting-edge targeted treatments, there is a solution for every patient.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, consult a specialist to explore your options. Early intervention and expert care can make all the difference in achieving the best possible outcome.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, feel free to contact us. Together, we can fight prostate cancer and move towards a healthier future.
